Spring面试题(三)
1. 什么是 Restful 风格的接口?
Restful(Representational State Transfer,表述性状态转移)是一种基于 HTTP 协议的 API 设计风格,核心是 “以资源为中心”,通过 HTTP 方法和 URL 表达操作意图,而非通过 URL 路径中的动词(如/addUser)。核心特征:
资源标识:用 URL 表示资源(如/users表示用户列表,/users/1表示 ID 为 1 的用户);
HTTP 方法语义:用 GET(查询)、POST(新增)、PUT(全量更新)、DELETE(删除)、PATCH(部分更新)表达操作;
无状态:每个请求包含完整信息,服务器不存储客户端状态;
响应格式:通常返回 JSON/XML,包含状态码(如 200 成功、404 资源不存在、500 服务器错误)。
示例:GET /users(查询所有用户)、POST /users(新增用户)、DELETE /users/1(删除 ID 为 1 的用户)。
2.Spring MVC 中的 Controller 是什么?如何定义一个 Controller?
Controller 是 Spring MVC 的核心组件,负责接收 HTTP 请求、处理业务逻辑、返回响应结果,是 “请求处理的入口”,本质是被 Spring IOC 容器管理的 Bean。
定义 Controller 的核心步骤:
类上添加 @Controller 注解(或 @RestController,后者包含 @Controller 和 @ResponseBody,适合返回数据而非视图);
方法上添加请求映射注解(如 @GetMapping/@PostMapping/@RequestMapping),指定处理的 URL 和 HTTP 方法;
方法参数接收请求数据(如 @RequestParam 接收 URL 参数、@RequestBody 接收请求体),返回结果(视图名或数据)。
示例:
java
// 传统Controller(返回视图)
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/list") // 处理GET请求:/user/list
public String getUserList(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("users", userService.getAllUsers());
return "user/list"; // 返回视图名(对应templates/user/list.html)
}
}
// RestController(返回数据)
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/user")
public class UserApiController {
@GetMapping("/{id}") // 处理GET请求:/api/user/1
public User getUser(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return userService.getUserById(id); // 返回JSON数据
}
}3.Spring MVC 中如何处理表单提交?
Spring MVC 处理表单提交需结合 “前端表单” 和 “后端 Controller 方法”,核心步骤:
前端表单:设置 method="post",action 指向 Controller 的请求路径,表单字段 name 与后端接收参数名一致;
示例(Thymeleaf 模板):
html
<form method="post" action="/user/save">
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="用户名">
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="密码">
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>后端处理:
方式 1:用 @RequestParam 逐个接收表单字段(适合字段少的场景);
java
@PostMapping("/user/save")
public String saveUser(@RequestParam String username, @RequestParam String password) {
userService.saveUser(username, password);
return "redirect:/user/list"; // 重定向到列表页
}方式 2:用 JavaBean 接收(适合字段多的场景),配合 @ModelAttribute(可选,自动将 Bean 存入模型);
java
@PostMapping("/user/save")
public String saveUser(@ModelAttribute User user) { // User类包含username、password字段及setter/getter
userService.saveUser(user);
return "redirect:/user/list";
}注意:若表单包含中文,需配置字符编码过滤器(如 CharacterEncodingFilter),避免中文乱码。
4.Spring MVC 中的视图解析器有什么作用?
视图解析器(ViewResolver)是 Spring MVC 中 “将逻辑视图名转换为物理视图” 的核心组件,作用是:
接收 Controller 返回的 ModelAndView 中的 “逻辑视图名”(如 user/list);
根据配置的规则(如前缀、后缀),拼接出物理视图的路径(如 classpath:/templates/user/list.html);
创建对应的 View 对象(如 ThymeleafView、JstlView),将 Model 中的数据渲染到视图中,生成最终的 HTML 响应。
Spring MVC 常用的视图解析器:
InternalResourceViewResolver:用于解析 JSP 视图,配置示例:
xml
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/> <!-- 前缀 -->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> <!-- 后缀 -->
</bean>ThymeleafViewResolver:用于解析 Thymeleaf 模板,Spring Boot 自动配置,默认前缀为 classpath:/templates/,后缀为 .html。
若 Controller 返回的是 @ResponseBody 注解的方法(返回数据),则不经过视图解析器,直接将数据转换为 JSON/XML 响应。
5.Spring MVC 中的拦截器是什么?如何定义一个拦截器?
拦截器(HandlerInterceptor)是 Spring MVC 中用于 “在请求处理前后执行自定义逻辑” 的组件,可实现权限校验、日志记录、请求参数预处理等功能,作用于 Controller 方法的调用链路中。
定义拦截器的核心步骤:
自定义拦截器类:实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口,重写 3 个核心方法;
java
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
// 请求处理前执行(如权限校验)
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
// 示例:未登录则重定向到登录页
if (request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser") == null) {
response.sendRedirect("/login");
return false; // 阻止请求继续执行
}
return true; // 允许请求继续执行
}
// 请求处理后、视图渲染前执行(如添加公共数据到模型)
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
if (modelAndView != null) {
modelAndView.addObject("currentTime", new Date()); // 所有视图共享currentTime
}
}
// 视图渲染后执行(如资源清理)
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
// 如关闭流、记录请求耗时等
}
}配置拦截器:在 Spring MVC 配置类中注册拦截器,指定拦截的 URL 路径和排除的路径;
java
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**") // 拦截所有路径
.excludePathPatterns("/login", "/register", "/static/**"); // 排除登录、注册及静态资源路径
}
}6.Spring MVC 中的国际化支持是如何实现的?
Spring MVC 国际化(i18n)支持是 “根据客户端 Locale(语言 / 地区)返回对应语言的页面或消息”,核心实现步骤:
准备国际化资源文件:在 resources/i18n 目录下创建多语言文件,命名规则为 basename_语言_地区.properties;
中文:messages_zh_CN.properties(如 user.login=登录);
英文:messages_en_US.properties(如 user.login=Login);
默认:messages.properties(未匹配到 Locale 时使用)。
配置国际化资源:在 Spring 配置类中配置 ResourceBundleMessageSource,指定资源文件基础名;
java
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
messageSource.setBasename("i18n/messages"); // 资源文件基础名(无需后缀)
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8"); // 编码
return messageSource;
}配置 Locale 解析器:指定如何获取客户端 Locale(如从请求参数、Session、Cookie 中获取);
常用 SessionLocaleResolver(Locale 存储在 Session 中,支持切换语言):
java
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
SessionLocaleResolver resolver = new SessionLocaleResolver();
resolver.setDefaultLocale(Locale.CHINA); // 默认Locale
return resolver;
}切换 Locale:通过 Controller 方法修改 Session 中的 Locale(如 request.getSession().setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, Locale.US))。
前端使用:在 Thymeleaf 模板中用 #{key} 引用国际化消息(如 <button>#{user.login}</button>)。
7.Spring MVC 中如何处理异常?
Spring MVC 提供 3 种核心异常处理方式,覆盖不同范围的异常场景:
局部异常处理(Controller 内部):用 @ExceptionHandler 注解,仅处理当前 Controller 抛出的异常;
java
@Controller
public class UserController {
// 处理当前Controller的NullPointerException
@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
public String handleNpe(Exception e, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("errorMsg", "空指针异常:" + e.getMessage());
return "error"; // 返回错误页面
}
}全局异常处理(所有 Controller):用 @ControllerAdvice + @ExceptionHandler,处理所有 Controller 抛出的异常;
java
@ControllerAdvice // 全局生效
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
// 处理所有RuntimeException
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public ModelAndView handleRuntimeException(RuntimeException e) {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("error");
mav.addObject("errorMsg", "运行时异常:" + e.getMessage());
return mav;
}
// 处理Rest接口的异常,返回JSON
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result handleBusinessException(BusinessException e) {
return Result.fail(e.getCode(), e.getMessage()); // 自定义Result类
}
}全局异常页面:通过配置 SimpleMappingExceptionResolver,将异常类型映射到指定错误页面,无需写 Java 代码;
java
@Bean
public SimpleMappingExceptionResolver exceptionResolver() {
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver resolver = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver();
// 异常类型 -> 错误页面
Properties mappings = new Properties();
mappings.setProperty("java.lang.NullPointerException", "error/npe");
mappings.setProperty("com.example.BusinessException", "error/business");
resolver.setExceptionMappings(mappings);
resolver.setDefaultErrorView("error/default"); // 默认错误页面
return resolver;
}8.Spring 中的 JPA 和 Hibernate 有什么区别?
JPA(Java Persistence API)和 Hibernate 是 “规范与实现” 的关系,核心区别: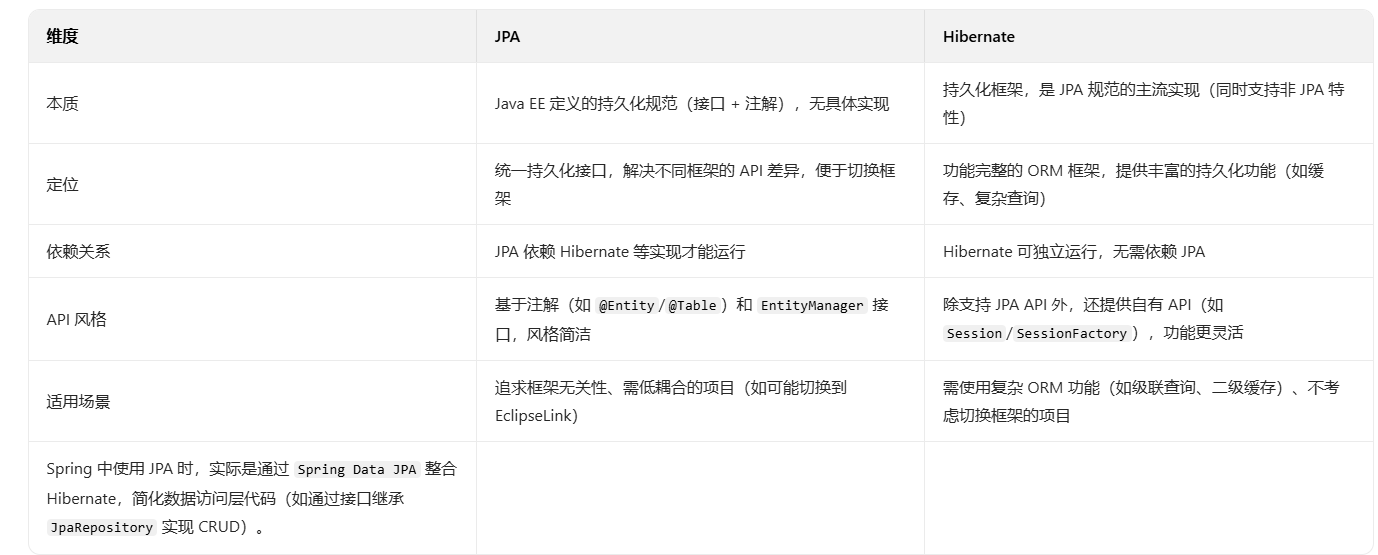
9.@Async 如何避免内部调用失效?
@Async 内部调用失效的原因是:同一类中方法 A 调用方法 B(B 有 @Async)时,调用不经过 Spring 动态代理对象,直接通过原始对象调用,无法触发异步逻辑。避免失效的核心思路是 “让调用经过代理对象”,具体方案:
注入自身代理对象:通过 @Autowired 或 ApplicationContext 获取当前 Bean 的代理对象,而非直接用 this 调用;
java
@Service
public class UserService {
// 注入自身代理对象(需开启Spring的代理暴露,默认开启)
@Autowired
private UserService userServiceProxy;
// 普通方法
public void process() {
// 用代理对象调用异步方法,避免失效
userServiceProxy.asyncMethod();
}
// 异步方法
@Async
public void asyncMethod() {
// 异步逻辑
}
}拆分服务:将异步方法抽取到独立的 Service 类中,当前 Service 注入该类的 Bean,通过注入的 Bean 调用异步方法;
java
// 独立的异步Service
@Service
public class AsyncService {
@Async
public void asyncMethod() {
// 异步逻辑
}
}
// 原Service
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
public void process() {
asyncService.asyncMethod(); // 调用独立Service的异步方法,无失效问题
}
}配置暴露代理:若注入自身代理对象失败,可在配置类添加 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true),通过 AopContext.currentProxy() 获取代理对象;
java
public void process() {
UserService proxy = (UserService) AopContext.currentProxy();
proxy.asyncMethod();
}10.@Async 什么时候会失效?
@Async 注解失效的核心原因是 “未触发 Spring 动态代理”,具体场景:
方法内部调用:同一类中用 this 调用异步方法(如 this.asyncMethod()),不经过代理对象,无法异步执行;
非 public 方法:@Async 仅对 public 方法生效,private/protected/default 方法的注解会被 Spring 忽略(因动态代理无法拦截非 public 方法);
未开启异步功能:未在配置类添加 @EnableAsync 注解,Spring 不识别 @Async,方法按同步执行;
方法返回值不合法:@Async 方法返回值只能是 void、Future 或 CompletableFuture,若返回其他类型(如 String、Integer),异步逻辑会执行,但返回值无法正确获取,且可能导致异常;
自定义线程池配置错误:若自定义线程池时未指定 TaskExecutor 的 Bean 名称为 taskExecutor,且未通过 @Async("poolName") 指定线程池,Spring 会使用默认线程池(SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor),但配置错误可能导致异步失效;
Bean 未被 Spring 管理:异步方法所在的类未添加 @Component/@Service 等注解,未被 Spring 扫描为 Bean,@Async 注解无效。
11. 在 Spring 中,拦截器和过滤器有什么区别?
拦截器(HandlerInterceptor)和过滤器(Filter)
均用于请求处理的增强,但属于不同层级,核心区别: